Run Shell scripts inside of your Flows
Run Shell scripts directly inside of your Flows and generate outputs.
You can execute bash script inside of a flow by either writing your Shell commands inline or by executing a .sh file. You can get outputs and metrics from your Shell script too.
Scripts
If you want to write a series of commands together to form a small script, and run that script as a task in the flow, you can use the io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Script.
id: shell_scriptnamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell script.
tasks: - id: shell_script_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Script containerImage: badouralix/curl-jq script: | # invoke a GET call on an API and extract information from the JSON response downloads=$(curl https://hub.docker.com/v2/repositories/kestra/kestra/ | jq -r '.pull_count') echo "Downloads: ${downloads}"You can read more about the Scripts type in the Plugin documentation.
Commands
You could also choose to provide the series of Shell commands in the task, and get the same result. Here is an example of how you can run the previous example using the io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands type:
id: shell_commandsnamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell commands.
tasks: - id: http_download type: io.kestra.plugin.core.http.Download uri: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kestra/datasets/raw/main/csv/orders.csv
- id: shell_commands_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands commands: - echo "The current execution is {{ execution.id }}" - cat {{ outputs.http_download.uri }}You can also put a Shell script in a separate .sh file, and invoke the script as a command. For example, we have a script file called hello.sh that contains:
echo "Hi there! This is an example of executing a Shell script file."sleep 2echo "I am back from sleep"You can now invoke this script as one of the commands in the io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands task. Note that we have set the enabled flag for the namespaceFiles property to true so Kestra can access the file.
id: shell_invoke_filenamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell script file.
tasks: - id: shell_invoke_file_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands namespaceFiles: enabled: true commands: - sh hello.shYou can read more about the Commands type in the Plugin documentation.
Handling Outputs
If you want to get a variable or file from your Shell script, you can use an output.
Variable Output
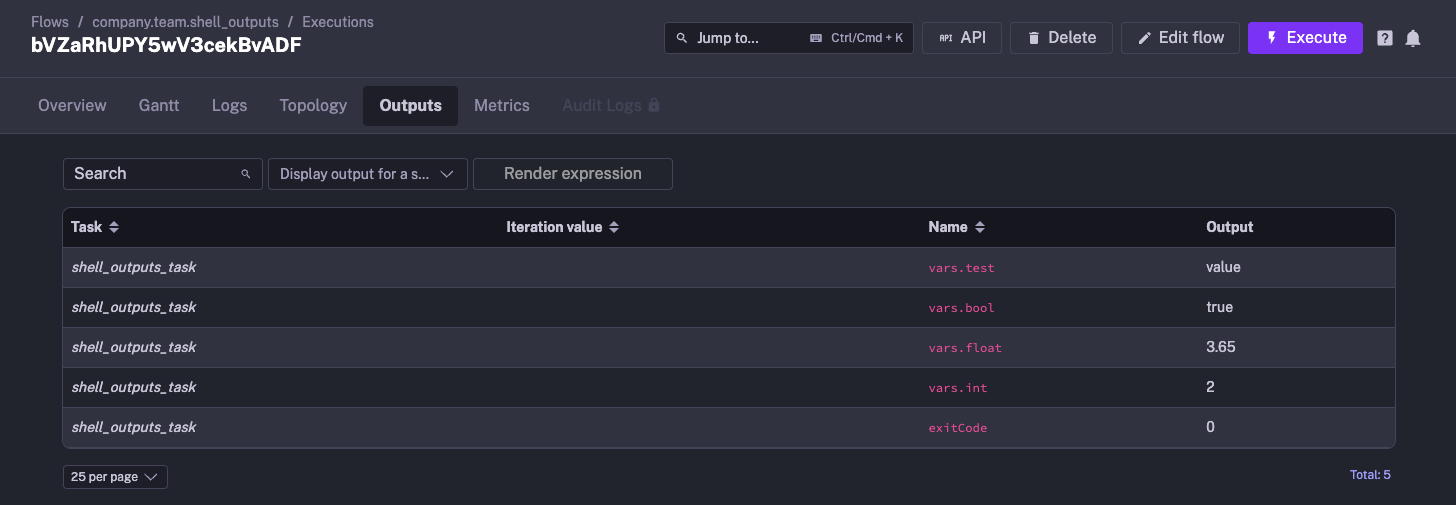
You can get the JSON outputs from the Shell commands / script using the ::{}:: pattern. Here is an example:
id: shell_outputsnamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell command, and outputs the variable.
tasks: - id: shell_outputs_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands commands: - echo '::{"outputs":{"test":"value","int":2,"bool":true,"float":3.65}}::'All the output variables can be viewed in the Outputs tab of the execution.
You can refer to the outputs in another task as shown in the example below:
id: shell_outputs_usagenamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell command, and outputs the variable.
tasks: - id: shell_outputs_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands commands: - echo '::{"outputs":{"test":"value","int":2,"bool":true,"float":3.65}}::'
- id: return type: io.kestra.plugin.core.debug.Return format: '{{ outputs.shell_outputs_task.vars.test }}'This example works for both io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Script and io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands.
File Output
Inside of your Shell script, write a file to the system. You’ll need to add the outputFiles property to your flow and list the files you’re trying to put out. In this case, we want to output output.txt. More information on the formats you can use for this property can be found in Script Output Metrics.
The example below writes a output.txt file containing the “Hello world” text, similar the output we used earlier. We can then refer the file using the syntax {{ outputs.{task_id}.outputFiles['<filename>'] }}, and read the contents of the file using the read() function.
id: shell_output_filenamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell command to output a file.
tasks: - id: shell_outputs_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands outputFiles: - output.txt commands: - echo 'Hello world' > output.txt
- id: log_output type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log message: "{{ read(outputs.shell_outputs_task.outputFiles['output.txt']) }}"This example works for both io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Script and io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands.
Handling Metrics
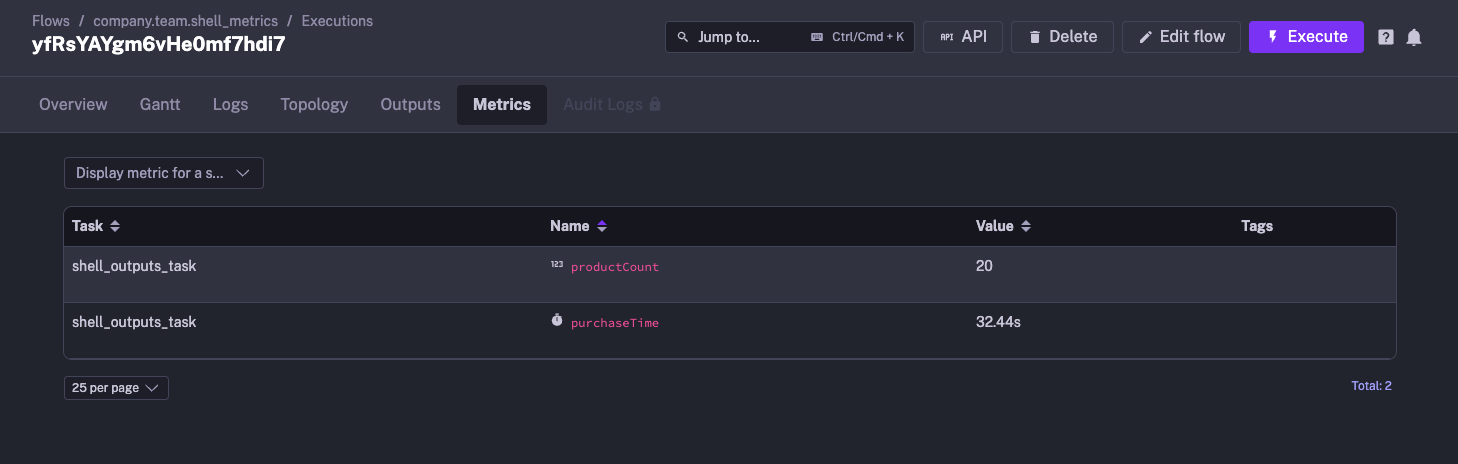
You can also get metrics from your Shell script. We use the same pattern for defining metrics as we had used for outputs ::{}::. In this example, we will demonstrate both the counter and timer metrics.
id: shell_metricsnamespace: company.teamdescription: This flow runs the shell command, and puts out the metrics.
tasks: - id: shell_outputs_task type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.shell.Commands commands: - echo 'There are 20 products in the cart' - echo '::{"outputs":{"productCount":20}}::' - echo '::{"metrics":[{"name":"productCount","type":"counter","value":20}]}::' - echo '::{"metrics":[{"name":"purchaseTime","type":"timer","value":32.44}]}::'Once this has executed, both the metrics can be viewed under Metrics.