Orchestrate dbt Workflows
Data teams use dbt to transform data in warehouses. While dbt simplifies SQL transformations, managing dependencies, testing changes, and deploying models at scale remains challenging. Kestra solves this by integrating dbt with your data platform through version-controlled workflows.
What is needed to orchestrate dbt workflows?
Orchestration platforms like Kestra automate the execution of dbt models while managing dependencies, environments, and deployments. With Kestra, you can:
- Version control models – Store dbt projects in Git and sync with Kestra’s namespace files
- Test changes safely – Run modified models in isolated containers before production
- Scale transformations – Execute dbt builds on dynamically provisioned containers in the cloud using task runners (AWS/GCP/Azure Batch)
- Integrate with your data stack – Chain dbt runs with ingestion tools, quality checks, and alerts.
Why Use Kestra for dbt Orchestration?
- GitOps Workflows – Sync dbt projects from Git, add and test new models, then push changes to Git from Kestra.
- Environment Management – Run models in different targets (dev/stage/prod) from one self-contained flow.
- Dynamic Scaling – Execute heavy dbt builds on serverless containers or Kubernetes clusters.
- Dependency Tracking – Automatically parse
manifest.jsonto visualize model relationships. - Integrated Testing – Add data quality checks between dbt models using Python or SQL.
- CI/CD Pipelines – Deploy model changes to multiple Kestra namespaces or Git branches.
- Multi-Project Support – Coordinate multiple dbt projects declaratively in one flow.
Example: dbt Project Orchestration
Below are common patterns to orchestrate dbt workflows using Kestra.
Fetch dbt Project from Git at Runtime
The example below shows a simple flow that runs dbt build for DuckDB in a Docker container. Note that the dbt project is cloned from a Git repository at runtime to ensure the latest version is used.
id: dbt_duckdbnamespace: company.team.dbt
tasks: - id: dbt type: io.kestra.plugin.core.flow.WorkingDirectory tasks: - id: clone_repository type: io.kestra.plugin.git.Clone url: https://github.com/kestra-io/dbt-example branch: main
- id: dbt_build type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI taskRunner: type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.runner.docker.Docker containerImage: ghcr.io/kestra-io/dbt-duckdb:latest commands: - dbt deps - dbt build profiles: | my_dbt_project: outputs: dev: type: duckdb path: ":memory:" fixed_retries: 1 threads: 16 timeout_seconds: 300 target: devSync dbt Project from Git to Kestra’s Namespace Files
You can sync the dbt project from a Git branch to Kestra’s namespace and iterate on the models from the integrated code editor in the Kestra UI.
id: dbt_buildnamespace: company.team.dbt
tasks: - id: sync type: io.kestra.plugin.git.SyncNamespaceFiles url: https://github.com/kestra-io/dbt-example branch: master namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}" gitDirectory: dbt dryRun: false
- id: dbt_build type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI containerImage: ghcr.io/kestra-io/dbt-duckdb:latest namespaceFiles: enabled: true exclude: - profiles.yml taskRunner: type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.runner.docker.Docker commands: - dbt build profiles: | my_dbt_project: outputs: prod: type: duckdb path: ":memory:" schema: main threads: 8 target: prodYou can use the above flow as an initial setup:
- Add this flow within Kestra UI
- Save it
- Execute that flow
- Click on the
Filessidebar in the code editor to view the uploaded dbt files.
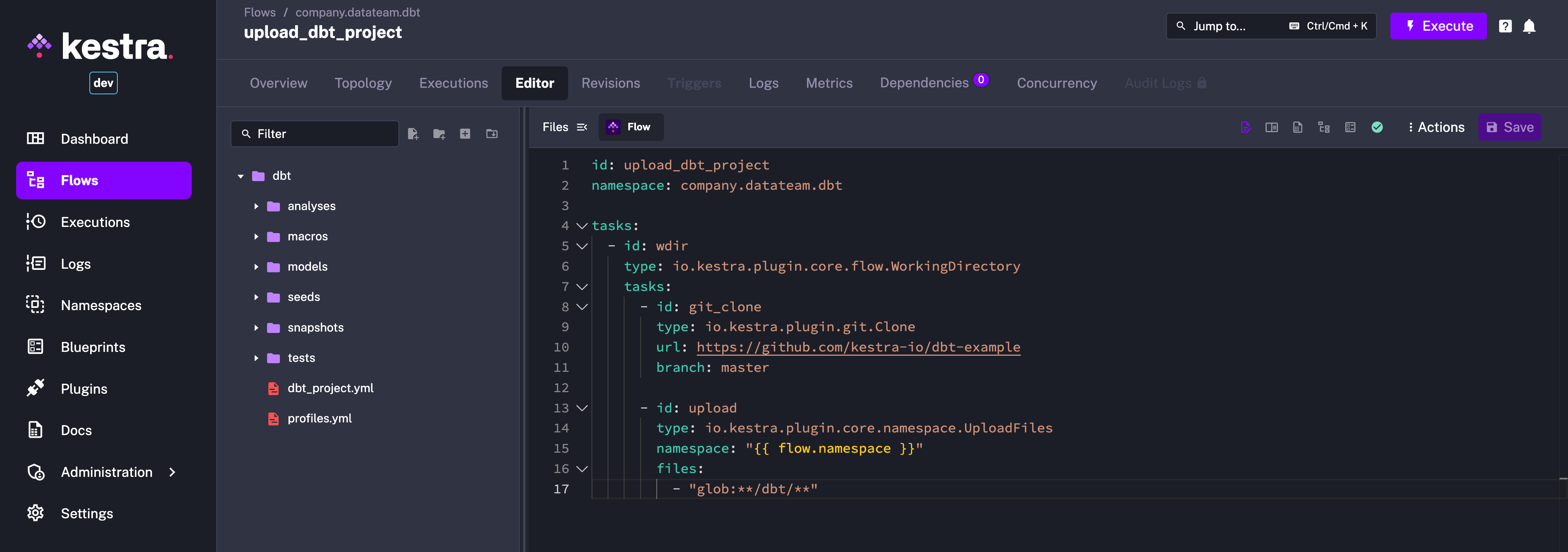
You can then set disabled: true within the first task after the first execution to avoid re-syncing the project. This allows you to iterate on the models without cloning the repository every time.
With the Code Editor built into Kestra, you can easily manage dbt projects by cloning the dbt Git repository, and uploading it to your Kestra namespace. You can make changes to the dbt models directly from the Kestra UI, test them as part of an end-to-end workflow, and push the changes to the desired Git branch when you are ready.
Run dbt CLI, iterate on models, and push changes to Git
Let’s create a flow that runs dbt CLI commands on top of the dbt project synced from Git to our Kestra namespace. We will use the Code Editor to make changes to the dbt models and push the changes back to the Git repository.
id: dbt_buildnamespace: company.team.dbt
inputs: - id: dbt_command type: SELECT allowCustomValue: true defaults: dbt build --project-dir dbt --profiles-dir dbt --no-partial-parse --target prod values: - dbt build --project-dir dbt --profiles-dir dbt --no-partial-parse --target prod - dbt build --project-dir dbt --profiles-dir dbt --no-partial-parse --target prod --select state:modified+ --defer --state ./target --target-path ./dev
tasks: - id: dbt type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI namespaceFiles: enabled: true containerImage: ghcr.io/kestra-io/dbt-duckdb:latest projectDir: dbt commands: - "{{ inputs.dbt_command }}" loadManifest: key: manifest.json namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}" storeManifest: key: manifest.json namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}" taskRunner: type: io.kestra.plugin.scripts.runner.docker.DockerNote how by using the namespaceFiles property, we can run dbt commands on the files uploaded to the namespace. This allows you to test the dbt models without having to clone the Git repository every time.
Execute the flow using the default value for the dbt_command input.
Edit dbt file
You can now open the dbt files in the Code Editor and make changes as needed. For example, let’s add a new model my_third_dbt_model.sql:
select *from {{ ref('my_first_dbt_model') }}where id = 2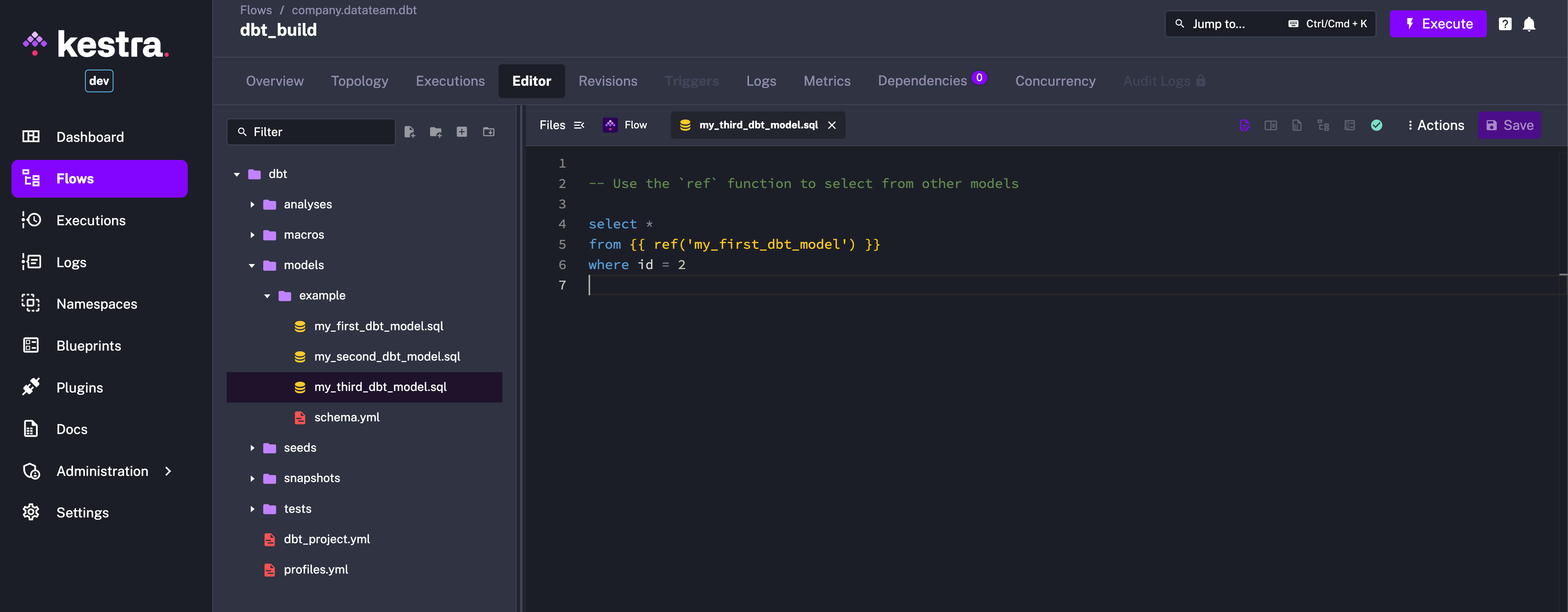
When you now run the flow using the second dropdown value for the dbt_command input, only the new model will be built. This allows you to test the changes quickly and iterate faster.
Push changes to Git
Once you are satisfied with the changes, you can push them to the same Git repository to your desired Git branch using the PushNamespaceFiles.
id: push_dbt_to_gitnamespace: company.datateam.dbt
inputs: - id: commit_message type: STRING defaults: "Changes to dbt from Kestra"
tasks: - id: commit_and_push type: io.kestra.plugin.git.PushNamespaceFiles namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}" username: git_username password: "{{ secret('GITHUB_ACCESS_TOKEN') }}" url: https://github.com/git_username/scripts branch: dev gitDirectory: dbt commitMessage: "{{ inputs.commit_message }}"Make sure to adjust the url, branch, and gitDirectory properties to match your dbt Git repository structure. If the branch does not exist, it will be created. If you want to test this step more incrementally, you can set the dryRun property to true to validate the changes before committing them to Git.
Kestra Features to Orchestrate dbt Workflows
Git Integration
Clone dbt projects from any Git provider:
- id: clone type: io.kestra.plugin.git.Clone url: https://github.com/kestra-io/dbt-example branch: mainBest-in-class log navigation across dbt models
Kestra automatically parses the manifest.json file within the Execution Gantt chart to provide visibility into each dbt model’s built status, their duration and logs. You can browse all logs in one place (without having to manually navigate to each dbt model) and you can easily jump to the next INFO/WARN/ERROR log thanks to the best-in-class log navigation feature.
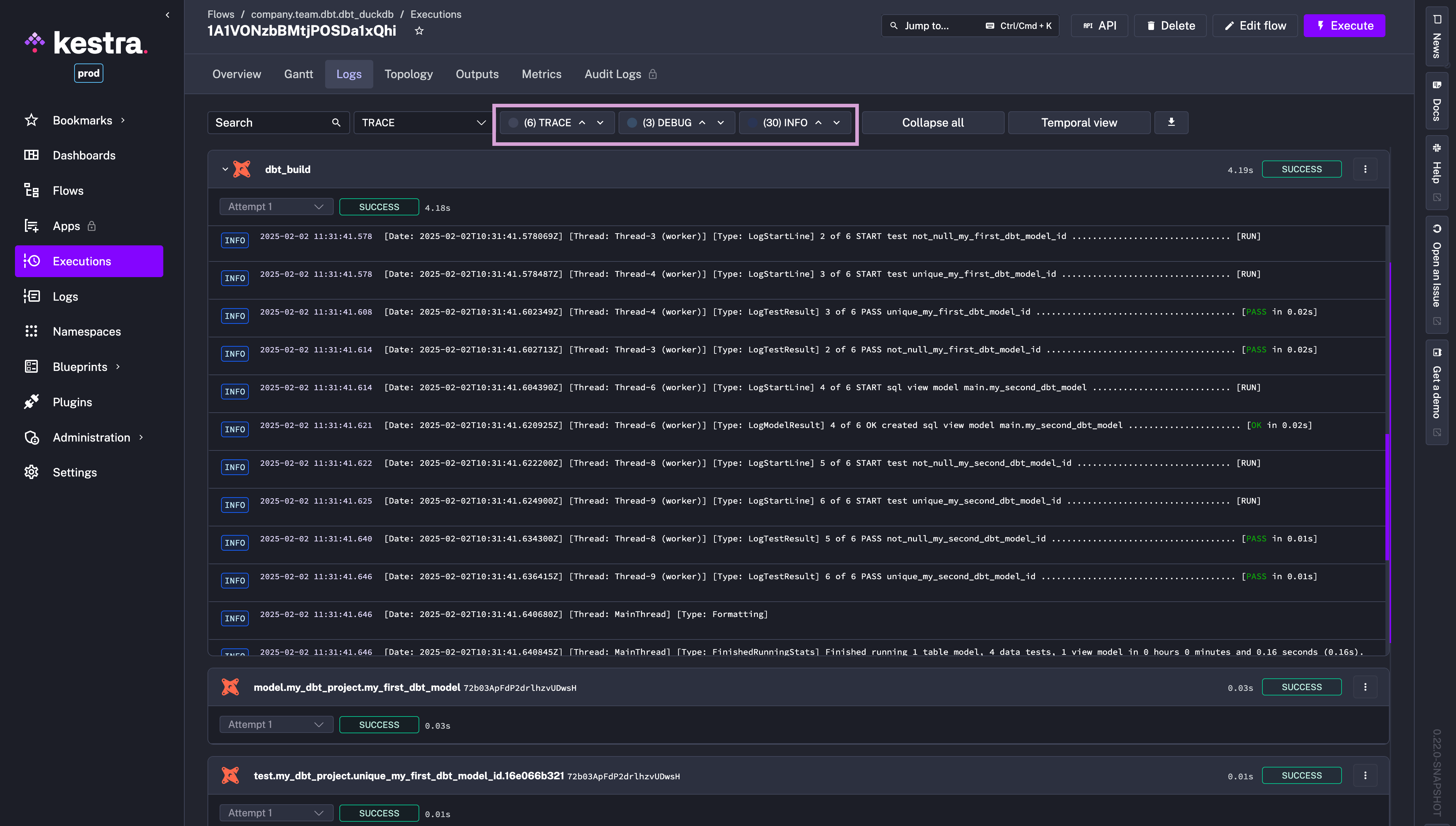
Manifest Tracking
Store dbt artifacts between runs in the integrated KV Store:
tasks: - id: dbt type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI namespaceFiles: enabled: true loadManifest: key: manifest.json namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}" storeManifest: key: manifest.json namespace: "{{ flow.namespace }}"Custom Quality Checks
Add quality checks validating dbt models using various plugins such as Soda:
- id: scan type: io.kestra.plugin.soda.Scan configuration: # ... checks: checks for orderDetail: - row_count > 0 - max(unitPrice): warn: when between 1 and 250 fail: when > 250 checks for territory: - row_count > 0 - failed rows: name: Failed rows query test fail condition: regionId = 4 requirements: - soda-core-bigqueryMulti-Project Coordination
If needed, you can orchestrate multiple dbt projects from a single flow:
- id: core type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI projectDir: dbt-core
- id: marts type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI projectDir: dbt-martsScale dbt Workflows in the Cloud
Adding the following pluginDefaults to that flow (or your namespace) will scale the dbt task so that the (computationally heavy) dbt parsing process runs on AWS ECS Fargate, Google Batch, Azure Batch, or Kubernetes job by leveraging Kestra’s task runners:
pluginDefaults: - type: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLI values: taskRunner: type: io.kestra.plugin.ee.aws.runner.Batch region: us-east-1 accessKeyId: "{{ secret('AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID') }}" secretKeyId: "{{ secret('AWS_SECRET_KEY_ID') }}" computeEnvironmentArn: "arn:aws:batch:us-east-1:123456789:compute-environment/kestra" jobQueueArn: "arn:aws:batch:us-east-1:123456789:job-queue/kestra" executionRoleArn: "arn:aws:iam::123456789:role/ecsTaskExecutionRole" taskRoleArn: "arn:aws:iam::123456789:role/ecsTaskRole" bucket: kestra-usYou can set plugin defaults at the flow, namespace, or global level to apply to all tasks of that type, ensuring that all dbt tasks run on AWS ECS Fargate in a given environment.
Getting Started with dbt Orchestration
- Install Kestra – Follow the quick start guide or the full installation instructions for production environments.
- Write Your Workflows – Configure your flow in YAML, declaring inputs, tasks, and triggers. Use one of the patterns above to sync dbt projects from Git, run dbt CLI commands, and push changes back to Git.
- Configure Environments — Set up dbt profiles for different targets based on your dbt project setup:
- id: dbttype: io.kestra.plugin.dbt.cli.DbtCLIcontainerImage: ghcr.io/kestra-io/dbt-duckdb:latestprofiles: |my_dbt_project:outputs:prod:type: duckdb
- Add Execution Triggers — Schedule dbt runs or trigger them based on upstream data availability:
triggers:- id: scheduletype: io.kestra.plugin.core.trigger.Schedulecron: "0 9 * * 1-5" # Weekdays at 9 AM
- Monitor Runs — Track dbt models and their execution durations in Kestra’s UI.
Next Steps
- Explore dbt plugins
- Read how-to guide on dbt
- Explore video tutorials on our YouTube channel
- Join Slack to ask questions, contribute code, report bugs and share and feature requests.
- Book a demo to discuss how Kestra can help orchestrate your dbt workflows.